Java Memory Management Explained: Heap, Stack, and Garbage Collection
Java applications rely heavily on efficient memory management to ensure performance and stability. Understanding how memory is allocated and managed is crucial for developers working on large-scale applications like AEM.
JVM Memory Parameters
When starting an AEM instance, you often see commands like:
java -XX:MaxPermSize=256m -Xmx1024M -jar cq-quickstart-6.3.0.jarKey Parameters
-XX:MaxPermSize=256m
Sets the maximum size for the Permanent Generation (PermGen) heap.
- Holds bytecode and metadata of classes.
- Separate from the object heap containing actual instances.
- Note: PermGen was removed in Java 8, replaced by Metaspace.
-Xmx1024M : Sets the maximum Java heap size (where objects live).
-Xms : Sets the Initial heap size.
-Xss : Sets Stack size per thread
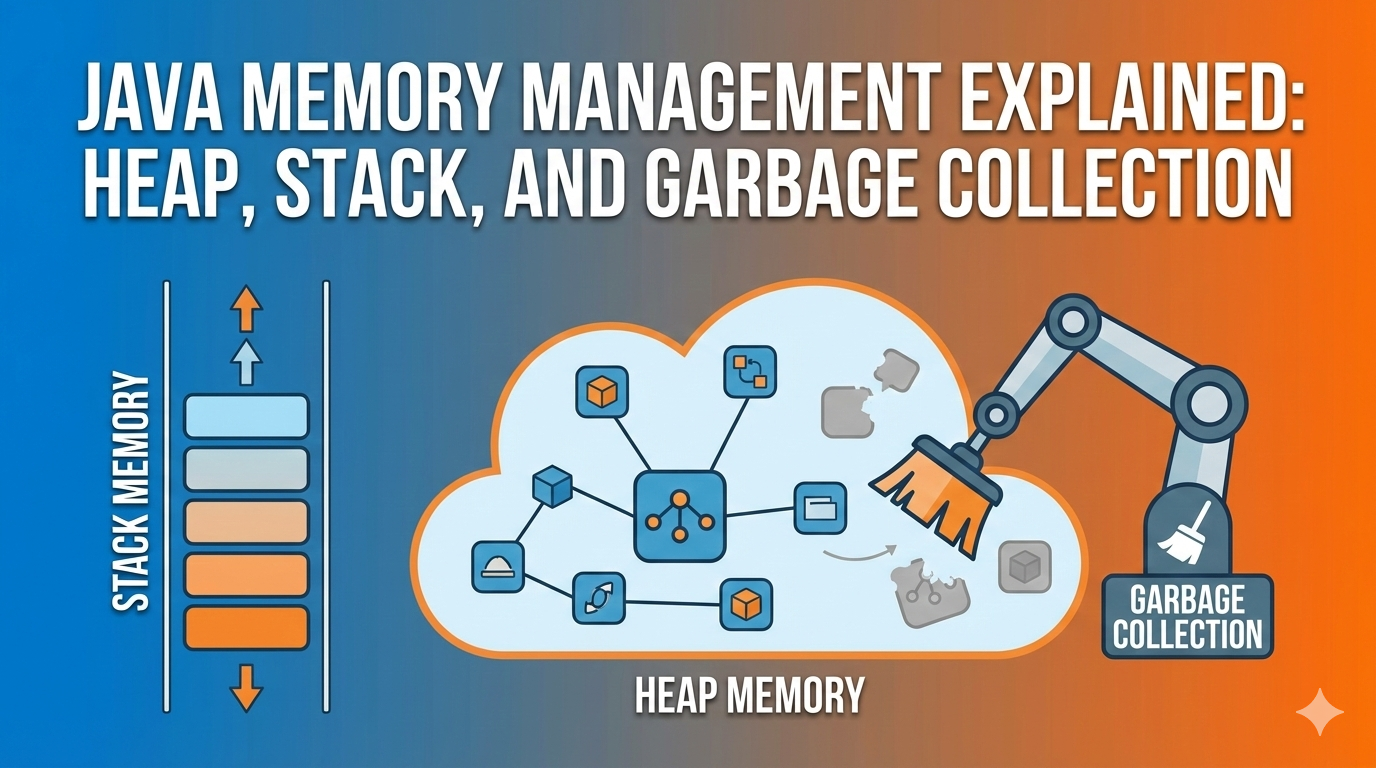
Heap vs Stack Memory
Heap Memory
- Used by all application threads.
- Stores objects and global data.
- Divided into:
- Young Generation (short-lived objects).
- Old Generation (long-lived objects).
- Accessible globally.
- Lives until the application ends.
- When full → OutOfMemoryError.
Stack Memory
- Used by a single thread.
- Stores:
- Local primitive variables
- References to objects in heap
- Very small and extremely fast.
- Short-lived (exists only during method execution).
- Organized in LIFO (Last-In-First-Out) manner.
- When full → StackOverflowError.
Garbage Collection (GC)
Java automatically manages memory using Garbage Collection:
Types of GC
Minor GC
- Works on Young Generation.
- Fast and frequent.
- Removes short-lived objects.
Major GC (Full GC)
- Works on Old Generation.
- Slower and can make the application pause.
- Cleans long-lived objects.
Memory Management in Java 8 and Later
- PermGen Removed: Replaced by Metaspace, which stores class metadata.
- Metaspace grows dynamically, reducing OutOfMemoryError risk.
- Tune Metaspace using: -XX:MetaspaceSize (initial size), -XX:MaxMetaspaceSize (maximum size).
Important Points
- Objects are always created in Heap; stack only holds references.
- Heap is large but slower, stack is tiny but fast.
- Proper tuning of ‘-Xmx’, ‘-Xms’, and ‘-Xss’ is critical for performance.
- Monitor GC logs to avoid long pauses during Major GC.
Tag
Java





Post Comment