Redux Saga: Middleware
As we discussed in a previous post, Redux is synchronous by nature. To handle asynchronous operations – such as making API calls – it requires the use of middleware. While Redux Thunk and Redux Saga are among the most popular choices for middleware, we are going to dive deeper into them here.
To recap, Redux is a centralized and predictable state container for JavaScript applications. It acts as a single source of truth, making state management easier to maintain. With its strong community support, extensive documentation, and vast ecosystem, Redux remains a staple in modern web development.
One of its most popular integrations is with React, achieved through the react-redux binding package. This combination allows developers to manage complex state in React applications efficiently.
Why Redux?
- Centralized State Management: All application state is stored in a single store.
- Predictability: State changes follow strict rules through actions and reducers.
- Debugging Ease: Tools like Redux DevTools make it easy to trace state changes.
- Community Support: Large ecosystem with plugins, middleware, and tutorials.
Handling Side Effects in Redux
By default, Redux operates synchronously. However, real-world applications often require asynchronous operations, such as API calls or delayed actions. Redux alone does not handle these side effects, so we need middleware.
Popular Middleware for Async Operations
Redux Thunk
- Allows writing functions (thunks) that dispatch actions asynchronously.
- Simple and easy to implement.
- Provides access to dispatch and getState inside the function.
Redux Saga
- Uses ES6 generator functions to manage side effects.
- Provides a more structured and testable approach.
- Ideal for complex async flows.
Generators in ES6
Generators are a key feature of ES6 and play an important role in Redux Saga. It is a special type of function that can pause execution and later resume from the same point.
function* myGenerator() {
yield 'Step 1';
yield 'Step 2';
}Keyword: yield is used to pause execution.
Benefits: Perfect for handling asynchronous flows in a synchronous-looking manner.
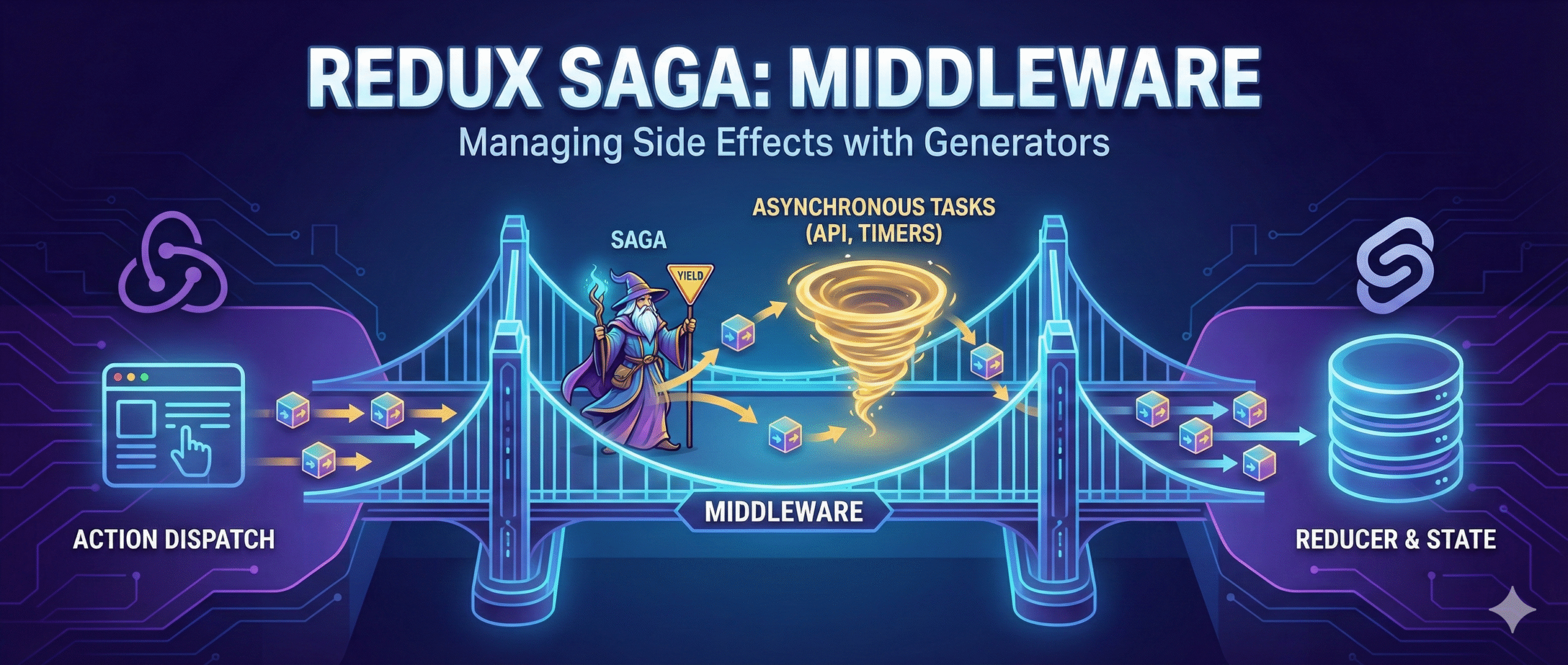
Redux Saga Overview
Redux Saga is a middleware for Redux that leverages ES6 generators to handle asynchronous operations elegantly.
Key Features:
- Full support for TypeScript.
- Makes complex async flows easier to read, write, and test.
- Provides powerful APIs for managing side effects.
Core Methods in Redux Saga
After adding Saga to the Redux store via middleware, you can intercept actions and perform async tasks using these methods:
- take: Listens for dispatched actions.
- put: Saga’s version of dispatch for triggering actions.
- call: Creates an effect to call a function with arguments.
- cancel: Cancels a previously forked task.
Error Handling in Redux Saga
Errors can be managed using try/catch blocks inside sagas. For example:
try {
const data = yield call(api.fetchData);
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_SUCCESS', payload: data });
} catch (error) {
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_ERROR', error });
}This allows dispatching error-specific actions and triggering fallback logic.
Alternatives: Redux Thunk
Redux Thunk is another middleware for handling async logic:
- Easier to set up.
- Allows writing functions that interact with the Redux store using dispatch and getState.
- Ideal for simple async flows.
Redux Saga vs Redux Thunk
| Feature | Redux Saga | Redux Thunk |
| Complexity | Better for complex flows | Simple use cases |
| Readability | Generators make code cleaner | Can become messy |
| Testing | Easier to test sagas | Harder to mock async logic |
| Learning Curve | Higher | Lower |
| Link | https://www.npmjs.com/package/redux-saga | https://www.npmjs.com/package/redux-thunk |
Why Choose Redux Saga?
- ES6 generators provide a clean, synchronous-looking approach to async code.
- Easier testing and debugging.
- Ideal for large-scale applications with complex side effects.





Post Comment