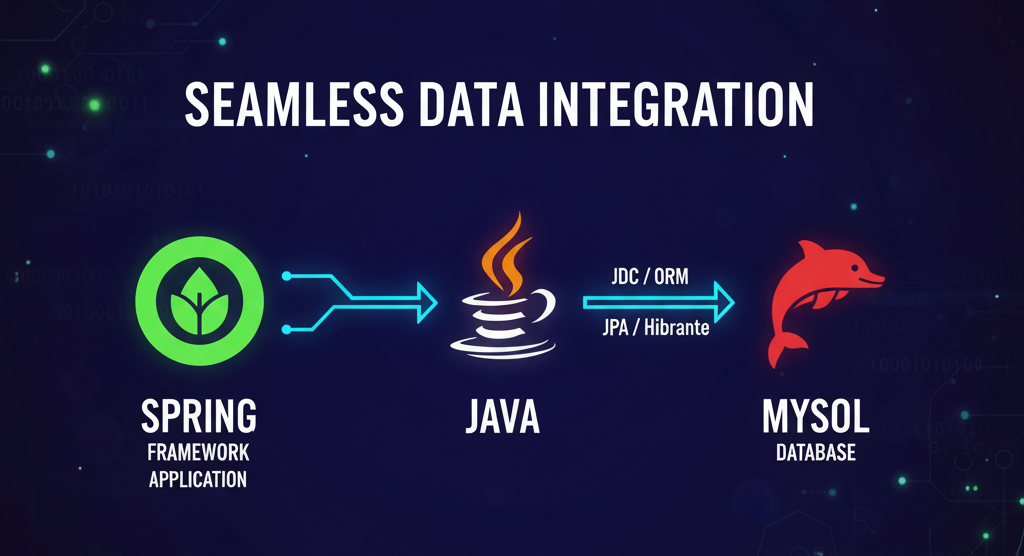
Spring: Database connection with MySQL
This is a walkthrough for establishing a connection between backend java code and database using spring boot.
First you need to set up the project for which you can use https://start.spring.io/, in this demo I have used 3.5.6 version of Spring Boot along with Java 21.
Add dependencies to your project based on your requirements. I am going to use JPA Repository to handle all my database related interactions and MySql as database.
This is how my POM looks like:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.5.6</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>in.stacknowledge</groupId>
<artifactId>sample</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>sample</name>
<description>Sample Application</description>
<url/>
<licenses>
<license/>
</licenses>
<developers>
<developer/>
</developers>
<scm>
<connection/>
<developerConnection/>
<tag/>
<url/>
</scm>
<properties>
<java.version>21</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-json</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-j</artifactId>
<version>9.4.0</version>
<scope>runtime</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-devtools</artifactId>
<scope>runtime</scope>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<annotationProcessorPaths>
<path>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</path>
</annotationProcessorPaths>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
Create an entities for your tables, following are the samples with relation to one another. To learn about what kinds of relationship we can have and how to manage them more browse through our blogs.
@Entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
@ToString
public class User {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long userId;
@Column(unique=true)
@NotNull
private String email;
@Column(unique=true)
private String mobile;
@NotNull
private String name;
@Column(columnDefinition = "boolean default false")
private boolean deleted;
@Enumerated(EnumType.STRING)
private Role role;
@ToString.Exclude
@OneToMany(mappedBy = "user", fetch = FetchType.LAZY, cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private List<Project> projects;
}
.......
public enum Role {
ADMIN, MANAGER, CLIENT, CUSTOMER
}
.......
@Entity
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Builder
public class Project {
@Id
@GeneratedValue(strategy = GenerationType.AUTO)
private Long projectId;
@ManyToOne
@JoinColumn(name = "user", referencedColumnName = "customerId")
private User user;
private String name;
private String detail;
}You can use lombok to ease your work with annotations like @AllArgsConstructor, @Data, @NoArgsConstructor, @Builder etc
Now create repository for your entity. You can add extra methods as per your requirements.
public interface UserRepository extends JpaRepository<User, Long> {
User findOneByEmail(String email);
User findOneByMobile(String mobile);
}Next is to create service to call repository and perform all the logic related task. We can do the same with controller but it is not considered as best practise.
@Service
public class UserService {
@Autowired
private UserRepository userRepository;
public User saveUser(final User user) {
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public User getUser(final long userId){
return userRepository.findById(userId).orElse(null);
}
public void deleteUserById(final Long userId){
Optional<User> userItem = userRepository.findById(userId);
if(userItem.isPresent()){
final User user = userItem.get();
user.setDeleted(true);
userRepository.save(user);
}
}
public User updateUser(final User user){
return userRepository.save(user);
}
public User getUserByEmail(final String email){
return userRepository.findOneByEmail(email);
}
public User getUserByMobile(final String mobile){
return userRepository.findOneByMobile(mobile);
}
public User buildUser(final String email, final String mobile, final String name, Role role){
if(role == null){
role = Role.CUSTOMER;
}
return User.builder()
.email(email)
.mobile(mobile)
.name(name)
.role(role)
.build();
}
}
Last part is to setup properties to establish connection. Open you application properties and add the following:
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto=update
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/stacknowledgedb
spring.datasource.username=user1
spring.datasource.password=i@mGroot
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.DriverFinally we can now test everything together by just running the spring application locally using this command.
mvn spring-boot:runAll the mentioned entities along with their relationship is now automatically created in your configured MySQL database. Now you can call your service from controller to perform the CRUD operations.





1 comment