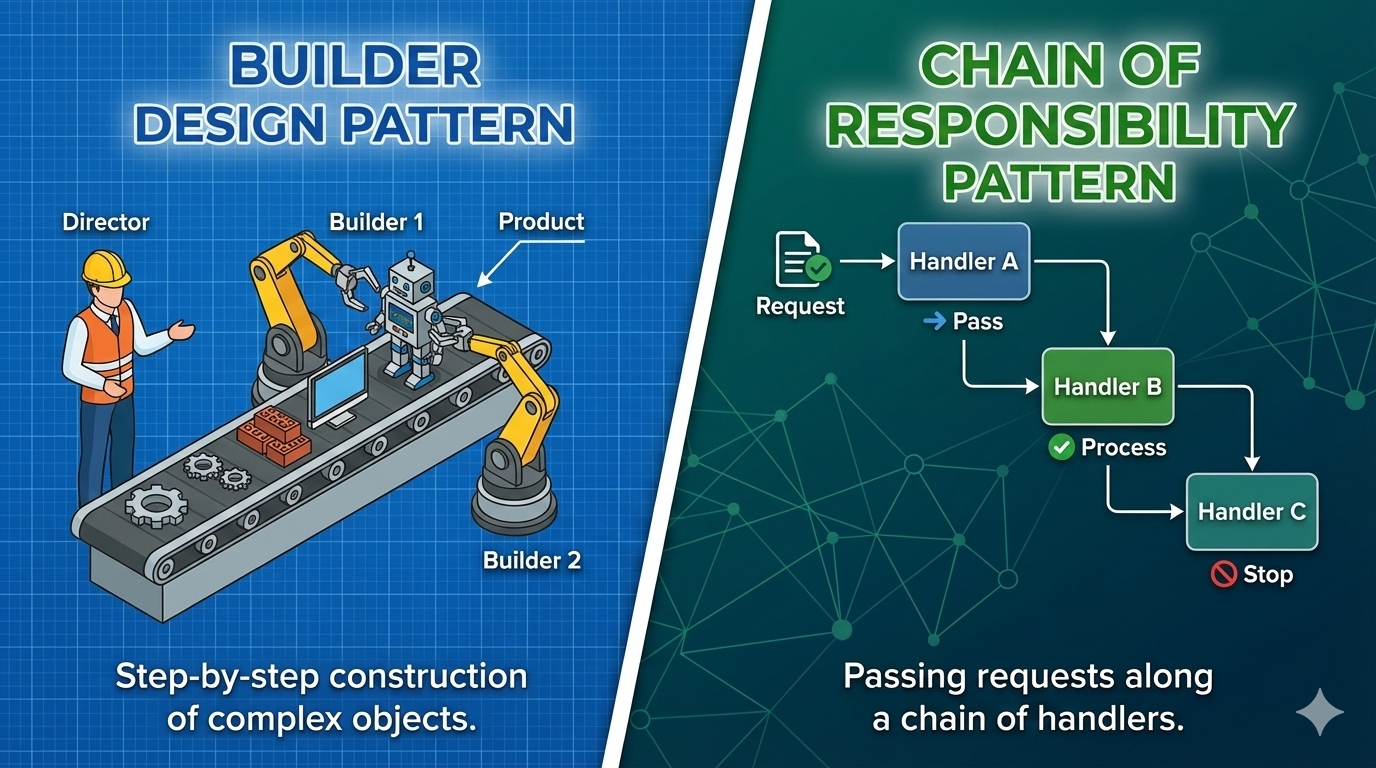
Builder Design Pattern vs Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Both patterns belong to the Gang of Four (GoF) design patterns but serve different purposes:
- Builder Pattern: A Creational Pattern for constructing complex objects step by step.
- Chain of Responsibility Pattern: A Behavioral Pattern for passing requests along a chain of handlers until one processes it.
Builder Design Pattern
Builder Pattern separates the construction of a complex object from its representation, allowing the same construction process to create different representations.
Structure
- Builder: Specifies an abstract interface for creating parts.
- Concrete Builder: Implements the steps.
- Director: Controls the construction process.
- Product: The final object.
class Car {
private String engine;
private String wheels;
private String color;
public void setEngine(String engine) { this.engine = engine; }
public void setWheels(String wheels) { this.wheels = wheels; }
public void setColor(String color) { this.color = color; }
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Car [engine=" + engine + ", wheels=" + wheels + ", color=" + color + "]";
}
}
interface CarBuilder {
void buildEngine();
void buildWheels();
void buildColor();
Car getCar();
}
class SportsCarBuilder implements CarBuilder {
private Car car = new Car();
public void buildEngine() { car.setEngine("V8 Engine"); }
public void buildWheels() { car.setWheels("Alloy Wheels"); }
public void buildColor() { car.setColor("Red"); }
public Car getCar() { return car; }
}
class Director {
public Car construct(CarBuilder builder) {
builder.buildEngine();
builder.buildWheels();
builder.buildColor();
return builder.getCar();
}
}
public class BuilderDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Director director = new Director();
CarBuilder builder = new SportsCarBuilder();
Car car = director.construct(builder);
System.out.println(car);
}
}Where to Use
- When creating complex objects with many optional parts.
- When object construction should be independent of representation.
Drawbacks
- Adds complexity for simple objects.
- Requires multiple classes (Builder, Director).
Chain of Responsibility Pattern
Allows a request to be passed along a chain of handlers. Each handler decides whether to process the request or pass it to the next handler.
Structure
- Handler: Defines an interface for handling requests.
- Concrete Handlers: Implement handling logic.
- Client: Initiates the request.
abstract class Handler {
protected Handler next;
public void setNext(Handler next) { this.next = next; }
public abstract void handleRequest(String request);
}
class AuthHandler extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("AUTH")) {
System.out.println("Authentication handled");
} else if (next != null) {
next.handleRequest(request);
}
}
}
class LogHandler extends Handler {
public void handleRequest(String request) {
if (request.equals("LOG")) {
System.out.println("Logging handled");
} else if (next != null) {
next.handleRequest(request);
}
}
}
public class ChainDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Handler auth = new AuthHandler();
Handler log = new LogHandler();
auth.setNext(log);
auth.handleRequest("LOG");
auth.handleRequest("AUTH");
}
}Where to Use
- When multiple objects can handle a request.
- When you want to decouple sender and receiver.
Drawbacks
- Hard to debug because the request may pass through many handlers.
- No guarantee that the request will be handled.
Similarities
- Both involve step-by-step processing:
- Builder constructs an object step by step.
- Chain processes a request step by step.
- Both decouple client from internal logic.
Differences
| Aspect | Builder Pattern | Chain of Responsibility Pattern |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Object creation | Request handling |
| Category | Creational | Behavioral |
| Output | A fully built object | A processed request or no action |
| Flow | Controlled sequence of building steps | Dynamic flow based on handler conditions |
Which to Use?
- Builder: When you need to create complex objects with many optional parts.
- Chain of Responsibility: When you need flexible request handling without hardcoding which handler processes it.
Drawbacks Summary
- Builder: Adds complexity for simple objects.
- Chain of Responsibility: Can make debugging harder and may leave requests unhandled.
Tag
Design Pattern Java





Post Comment